The demand for free higher education is one of the key factors that have led to competing waves of thinking and organisation in the sector.
Shutterstock
For over two decades South African higher education has been dominated by three successive and contending waves of thinking and organisation. They are: neo-liberal managerialism the decolonialisation of knowledge
and, most recently, the idea of a Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR).
By promising to “transform” higher education, each has taken centre stage at universities – or sections of them – by pledging greater value for the taxpayer (neo-liberalism); social emancipation (decolonisation); or greater access to employment (4IR).
The first wave follows Ronald Reagan’s “reform” of the Californian system which saw decreased state funding for universities. This was taken up by UK Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher. Her funding policies encouraged British universities to adopt business management practices. It also involved gearing degree offerings to the requirements of “the market”.
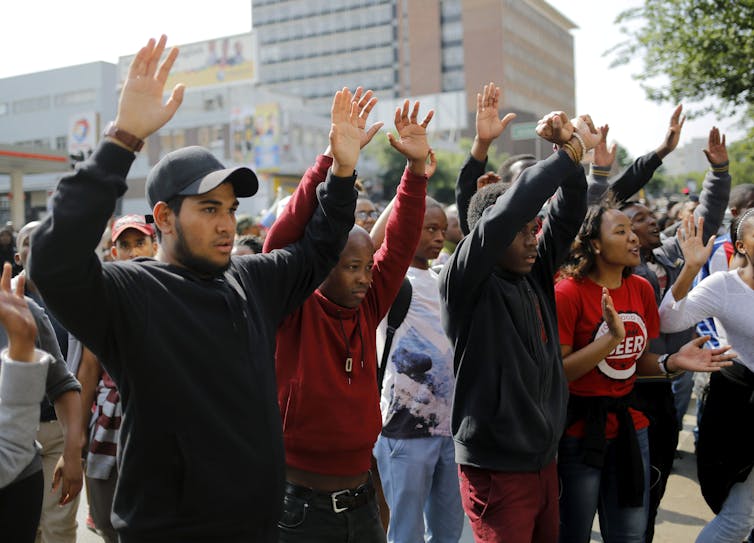
In South Africa, the second was symbolised by the March 2015 protest at University of Cape Town over the stature of Cecil John Rhodes. The movement has been marked by (sometimes violent) demands for a reform of curriculum away from the western “canon” and towards African epistemologies. Politically, it has been characterised by demands for free higher-education.
The third has been propagated by the World Economic Forum and across the world by the champions of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the digital revolution. In South Africa this wave has been promoted especially by the University of Johannesburg. This perspective holds that AI and machine-learning will dominate knowledge and knowledge-creating deep into the present century. All academic disciplines should, therefore, be geared to this end.
But there has been very little public discussion about the contradictions between the three moments.
South African higher education remains remarkably detached from society. Its loss of a social purpose can be seen as the erosion of the public and civic vitality which once fuelled the anti-apartheid struggle. Today, its mission has shrunk.
Why is there this disconnect?
The answer is simply that policies and incentives disadvantage the deep connection with the communities in which universities are located. They also emphasise peer-reviewed articles in internationally ranked journals as the measure of excellence. And they lead to a focus on educating students for high-paying jobs. They have little to do with positioning the welfare of society at the core of their scholarship, teaching, and public connections.
Put differently, higher education in the country doesn’t fulfil its civic potential. It has no real social purpose.
There are contrasting examples internationally. For instance, Tokai University, the leading STEM university in Japan, has a vision and mission grown from its founder’s philosophy – Professor Shigeyoshi Matsumae. His life goal was to create a university where young people and faculty would have sustained, deep interactions with social purpose.
Tokai University is implementing this philosophy. It has intensive citizenship education on all eight of its regional campuses for 7,000 entering first year students. It plans to expand this to 30,000.
The true purpose of universities
In the minds of faculty, administrators, government and business leaders, South African universities service two important, but limited, activities.
The first is to prepare students for jobs. The second is to conduct research that treats social communities more as objects of study than as knowledge partners. This approach excludes the development and support of civic agency from scholarly purpose.
Even disciplines that encourage research aimed at enhancing well-being – economics, is the best and worst example
– are deeply flawed. The emphasis is on technical skills and emulating models of prosperity that are based on individual rational choice as the motivator of human agency.
The hard truth is that higher education contributes to societal erosion when expert-knows-best approaches displace civic agency. This is because experts are often far removed from the needs of community development.
Alarmingly, too, teaching and research with public purpose have been squeezed out.
Higher education which prepares students for res publica – for the community – or in local terms, ubuntu – the community-confirming idea that we are human because of other humans – has been replaced. Instead what South Africa has is education suited for a res idiotica – in the Greek, a private and isolated person.
What can be done?
Fortunately, a growing literature points towards strands of civic revival in higher education. And there are a growing number of examples of a recovery of civic and democratic purposes in higher education.
Moreover, two broad streams of thinking are establishing new platforms for exchange, experiment, and social change. One is an interdisciplinary and transdisciplinary field that has emerged under the broad rubric of “Civic Studies”.
This encourages research and real-world projects which integrate empirical, cultural, and political knowledge as resources for community agency, societal co-creation and human flourishing. One example is the US-based Anchor Institution Task Force. This involves more than 700 universities and colleges which use their economic, physical and educational resources for community development.
One of the key elements of civic studies is public work, a framework of social action developed in partnership with other organisations. These include the Institute for Democracy in South Africa and other international partners.
Cultural evolution is the other stream. This provides resources for civic reconstruction of higher education. Key to this approach is the work of the late Nobel Laureate Elinor Ostrom, a co-founder of civic studies. Working with a network of international colleagues on collective governance of common pool resources, she refuted the rational individualism which has held sway over a great deal of social science across the world.
Her work helped in the translation of cultural evolution science to meet the challenges of improving human societies.
Civic studies and cultural evolution show that human societies can succeed through cooperative efforts within and across groups. But this is only possible when members understand and pursue their interests with conscious regard for the well-being of all.
Higher education needs to take on this insight because it’s indispensable for revitalising human agency, flourishing communities, and active democracy.
It will also re-frame scholarship, teaching and public engagements. This needs to be in pursuit of ensuring that scholarship becomes an integral part of democratic life, not simply as a partner with society.
Peter Vale, Senior research fellow, Centre for the Advancement of Scholarship, University of Pretoria and Harry Boyte, Senior Scholar in Public Work Philosophy, Augsburg University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license.